Please don't ignore the precancerous lesions on the skin.
Many elderly people's face and neck grow "color spots" that is "age spots", relax their vigilance, but they do not know that many "age spots" hide a kind of skin cancer prelesions, called solar keratosis. Solar keratosis is the skin damage caused by long-term sun exposure or other radiation damage, also known as actinic keratosis. The disease has a long course and sometimes develops into squamous cell carcinoma. The disease is more common in the elderly, but in areas with severe sun exposure, the disease can also occur in people aged 20 to 30. The main manifestations are local color and texture changes of the skin. It usually occurs on the head, face, back of hand, forearm and other light-exposed parts.
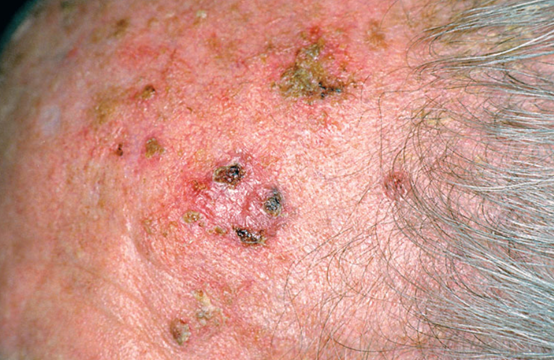
1. What are the clinical manifestations of solar keratosis?
It initially appears as a pale red or grayish white round, irregular keratinized papule with clear boundaries. The surface is rough and attached to dry scales. Most of the skin lesions have obvious sun damage, manifested as dry skin, wrinkle, atrophy and telangiectasia.
2. Why do I get solar keratosis?
The pathogenesis of the disease is complex, the occurrence of the disease is related to their own gene mutation and excessive exposure to ultraviolet light, and the abnormal proliferation of skin cells causes the disease.
3. What causes solar keratosis?
(1) Personal factors: previous history of skin tumors: individual sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation will increase the risk of this disease. Immune system dysfunction: Patients with long-term use of systemic immunosuppressive drugs have a higher prevalence. Age: The prevalence of solar keratosis increases with age.
(2) Environmental factors: long-term skin exposure to ionizing radiation, thermal radiation, ultraviolet radiation, asphalt and coal tar products.
4. When do I need prompt medical attention?
(1) In the case of scattered papules or erythema on the skin after sunburn with scales attached to the surface, further examination under the guidance of a doctor is required.
(2) The skin appears tan or dark brown rash, keratosis is serious, need to seek medical attention in time.
(3) Skin erosion, ulcer, need immediate medical attention.
5.What tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis?
(1) Physical examination: mainly according to the characteristics of the rash and the degree of skin lesions as the basis for diagnosis.
(2) Skin biopsy: Pathological diagnosis is an important diagnostic indicator to clarify the pathological classification.
(3) Dermoscopy: The diagnosis of solar keratosis has a high sensitivity and specificity to judge the benign and malignant lesions.
6.How can this precancerous lesion be treated?
The main treatment methods include topical drugs, physical therapy and surgical excision. The purpose is to control the expansion of the lesion, promote healing of the damaged area or remove the lesion. The disease requires long-term intermittent treatment. After formal treatment, the disease can be obviously controlled, reduce the possibility of malignant changes, and reduce the recurrence rate. The patient can return to normal life and the prognosis is good. Without treatment, the skin lesions can become malignant and progress to squamous cell carcinoma. In addition, regular visits are needed to check the skin for cancerous changes. The specific interval depends on the severity of the patient's condition, or as prescribed by the doctor.
Author:
Sun Xiaoyan
Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology
(The views expressed are those of the author)

