Opinions on "Swelling" Differ — — General Practitioners Come to Answer "Swelling" Questions for You
In daily life, there are always elderly people who say that their feet are swollen, hands are swollen, faces are swollen, eyes are swollen, and even the whole body is swollen, and today we will talk about how the elderly "swollen" is going on.
Edema is a common clinical symptom, which refers to excessive fluid retention in the tissue space or body cavity. According to the distribution of edema, it is mainly divided into systemic edema and local edema. According to whether the edema is depressed after pressing, it can be divided into depressed edema and non-depressed edema.
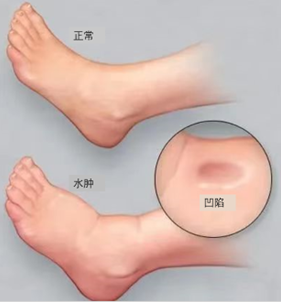
How to assess the degree of edema?
The most common and easiest way to do this is to measure body weight and limb circumference.
In general, for non-depressed edema, usually more than 10% weight increase, edema will occur. Unilateral limb edema should be compared with the opposite limb. For the lower limb, a change of 1 cm in the diameter of the ankle or 2 cm in the lower leg over the last week should be considered for edema.
For depressed edema, the latest method is to use the Wiese edema severity grading method: press the edema site for 5 seconds, relax the pressure, and divide depressed edema into 4 grades according to the time of skin return to normal: Grade I <30 seconds, Grade II 30~59 seconds, grade III 60~89 seconds, and grade IV 90~120 seconds.

The elderly should pay attention to: different parts of the swelling, suggesting different reasons.
1. Lower limbs are swollen first, pay attention to heart problems: cardiogenic edema is concave, and edema first appears in both lower limbs or low hanging parts (obvious in the sacrococcygeal tail and buttocks when lying down). In people with severely impaired heart function, edema can even progress to the face. Usually pay attention to high feet when sitting, and high heels when lying flat to ensure venous blood return and reduce edema.
2. Eyelid swelling first, pay attention to kidney problems: nephrogenic edema is depressed, if you did not drink too much water the night before, and the upper and lower eyelids are swollen when you get up in the morning, you should pay attention to kidney problems. It is recommended to do kidney function, urine routine, kidney B ultrasonography and other further tests.
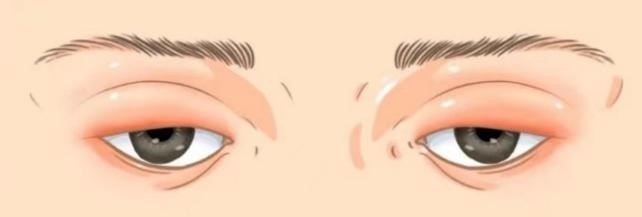
3. The face is swollen, pay attention to thyroid problems: edema caused by thyroid abnormalities is mostly non-depressed, that is, it is not easy to have obvious depression when pressed. When thyroid function is low, it is easy to appear edema of the face and hands and feet, and the skin is pale; In hyperthyroidism, swelling of the eye tissue and protrusion of the eyeball are likely to occur. At this time, it is recommended to check thyroid function and thyroid B-ultrasound.
4. Swollen ankles, bloated stomach, beware of liver problems: hepatogenic edema The ankle appears first, and gradually spreads upward, while the head, face, and upper limbs are usually not edema. Edema caused by cirrhosis may even be accompanied by ascites, varicose veins, etc. The common causes of cirrhosis include viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, fatty liver disease, schistosomiasis liver disease, etc.
5. General edema, may be malnutrition: the elderly due to disease, aging or other reasons to eat too little for a long time, there will be malnutrition, and the lack of nutrients, especially the lack of protein can cause systemic edema, generally occurs slowly, starting from the loose tissue, serious low-hanging parts such as lower limbs edema. In addition, vitamin B1 deficiency can also cause edema.
6. Unilateral limb swelling, beware of lymphatic abnormalities: lymphoedema is non-pitted edema. Primary lymphedema may be associated with lymphatic fiber obstruction, dilatation and systolic emptying dysfunction. The common causes of secondary lymphedema include lymphadenectomy, fibrosis after radiotherapy, tumor infiltration of lymph nodes or obstruction of lymphatic vessels by tumor cells, filariasis, etc.

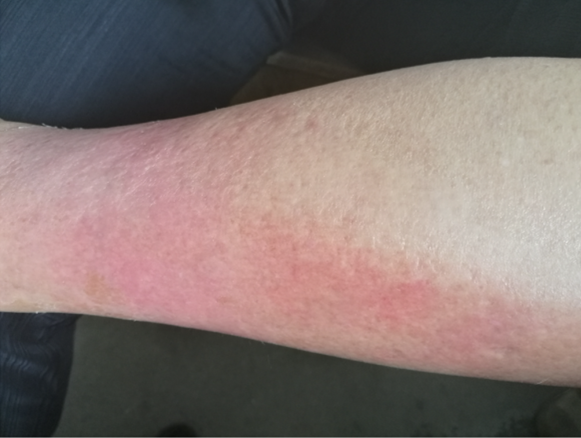
7. Local red swelling heat pain, inflammatory edema is common: there is tissue fluid exudation in the inflammatory area, containing a large number of proteins and inflammatory cells, which is the most common clinical localized edema. Common diseases are erysipelas (caused by hemolytic streptococcal infection), which occurs in people with low immunity, people with local skin lesions on the body surface, and people with chronic underlying diseases, especially patients with diabetes and poor blood sugar control.
8. Eyelid edema with purplish red spots, alert to dermatomyositis: If there is unique skin damage such as edema purplish red spots, finger extension purplish papules and skin heterochromia, and accompanied by symmetric muscle weakness, pain, dysphagia, etc., to consider dermatomyositis.

9. There are other causes of edema:
1) Edema caused by drugs: such as non-steroidal analgesics (such as aspirin), calcium antagonists (such as amlodipine, nifedipine), adrenal corticosteroids (such as methylprednisolone tablets), testosterone, estrogen, insulin, etc. Edema usually occurs after medication and disappears after discontinuation.
2) Venous obstructive edema: can be divided into upper vena cava obstruction syndrome and lower vena cava obstruction syndrome, the former is the main sign of eyelid edema, early symptoms accompanied by headache, vertigo, the latter is characterized by lower limb edema. And limb vein thrombosis and thrombophlebitis.
3) Allergic edema: edema occurs more suddenly, often have a history of allergy. The edema usually subsides quickly after symptomatic treatment (such as anti-allergy therapy).
4) Functional edema: mainly includes edema caused by high temperature environment, obesity edema, senile edema, traveler edema, sedentary edema, etc., often without the underlying diseases causing edema.
How to treat edema?
Edema caused by disease should be treated in time, and changing some bad habits can also help reduce swelling.
1. Medication: Medication is the most effective way to relieve symptoms. Commonly used drugs are mainly diuretics (such as furosemide, spironolactone, hydrochlorothiazide, tolasemide, etc.) and dehydrating agents (mannitol, etc.). It should be used under the guidance of a doctor, and at the same time, attention should be paid to the adverse reactions of drugs, to avoid the occurrence of electrolyte disorders, and regular monitoring of blood electrolyte.
2. Non-drug treatment: It is recommended to make improvements in living habits, diet and other aspects. 1. Avoid standing for long periods of time. Get up and move around regularly. 2. Before you go to sleep, raise your lower limbs above the height of your heart. 3. Light diet, controlMake salt, eat more fresh vegetables and fruits. Can moderately eat some high potassium, diuretic, iodine containing foods: high potassium foods haveMushrooms, spinach, broccoli, celery, beetroot, bananas, tomatoes, apples, etc., can promote the discharge of sodium; Diuretic foods include winter melon, cucumber, watermelon, pomegranate, grape, corn beard tea, etc. Iodine containing foods include kelp, shrimp and so on. Don't wear it too tight Wear clothing, elastic socks and avoid high heels.
3. Active treatment of the primary disease: edema is a symptom, not a disease diagnosis, there are many reasons for edema, and the degree of edema is closely related to the primary disease. It is necessary to identify the cause of edema and actively treat the primary disease, which can significantly improve the edema. It is recommended that patients can go to the general clinic for consultation, and the general practitioner can obtain detailed information and then conduct diagnosis and treatment guidance. Some elderly people take many oral drugs, and for drug-induced edema, it is especially necessary for the general practitioner to provide reasonable personalized prescription.
Edema trouble, go to the doctor in time. Eat a light diet and raise your feet appropriately.
Be careful with your medicine. Don't claim it yourself. Investigate the cause carefully and remove the swelling.
Author:
Yao Bilian: Department of General Medicine, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine; Health Manager, public dietitian, case manager
Ye Chenjing: Deputy chief physician of Ruijin Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Youth member and Secretary of Hematology Branch of Chinese Geriatrics Society
(The views expressed are those of the author)

