Interpretation of basal cell carcinoma of the skin, so that you no longer talk about "cancer" discoloration
Tips: The pictures in this article may cause discomfort.
1. What is skin basal cell carcinoma?
basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common malignancy in dermatology. In China, about 400 out of every 100,000 people get sick. BCC grows slowly and rarely metastasizes, but it sometimes grows locally infiltratively, destroying tissues and organs, leading to organ dysfunction, and can even be life-threatening.
2. Why do I get BCC?
There are many risk factors for BCC, among which ultraviolet exposure is the most important environmental factor.
Light skin color, multiple sunburns, and aging are all potential risk factors for BCC. People with a family history of skin cancer, immunosuppressive conditions such as HIV infection or after organ transplantation, exposure to ionizing radiation and chemical carcinogens (especially arsenic) are also at increased risk of BCC. In addition, some genetic diseases such as xeroderma pigmentosa and cutaneous albinism are also risk factors for BCC.
3. What should I do in case of illness?
Patients suspected of having BCC must go to a regular hospital for diagnosis, once diagnosed, do not be afraid, follow the doctor's guidance, and carry out standardized treatment.
There are five clinical types of BCC: nodular type, superficial type, maculoid/infiltrating type, pigmented type and fibroepithelioma type. In addition, nevoid BCC syndrome and Bazex syndrome are also included. Different types of BCC have different risk levels, so it is best to have an excision biopsy and histopathological examination, which is the gold standard for the diagnosis and classification of BCC.
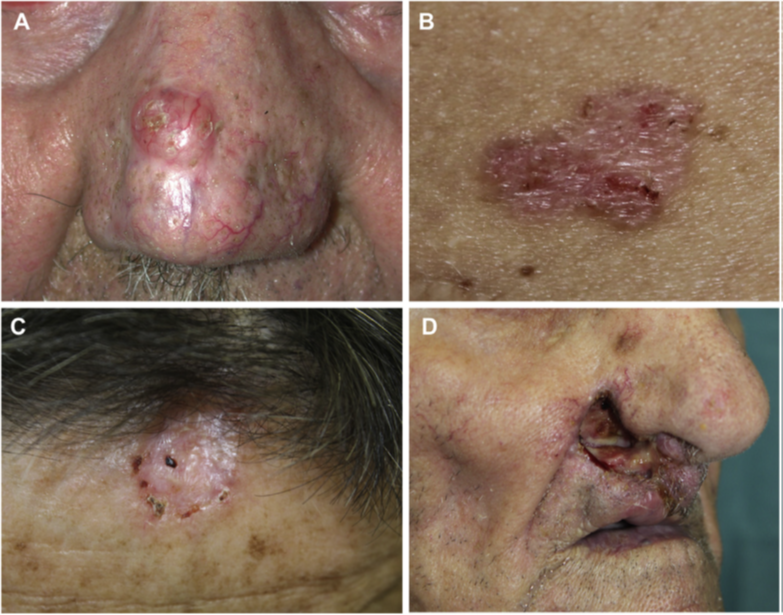
The clinical manifestations of BCC are: A. nodular; B. Superficial type; C. Infiltration type; D. Ulcer type [1]
After diagnosis of BCC, following the guidance of doctors, BCC was classified into high-risk or low-risk types according to factors such as lesion site, lesion size, boundary, primary or recurrent occurrence, immunosuppression, previous radiotherapy site, pathological type, and perineuronal infiltration.
The preferred treatment for BCC is surgical excision, including standard surgical excision and Mohs surgery. Non-surgical treatments such as electrodesiccation and curettage, topical drugs, photodynamic therapy, cryotherapy and radiotherapy can also be combined to improve tumor clearance and reduce the incidence of adverse reactions. The specific treatment plan needs to be discussed with the attending doctor to decide oh!
4. What should I pay attention to after treatment?
Can skin basal cell carcinoma cancer be cured? Many patients in the ward listen to ";cancer"; color change, can not help but cry.
In fact, standardized diagnosis and treatment, active follow-up, BCC is not invincible. BCC lesions usually grow slowly and rarely metastases, with a metastasis rate of only 0.0029% to 0.55%. The 5-year cure rate of low-risk BCC is above 95%. After the first BCC treatment, about 80% of patients will relapse within 5 years. When local recurrence is suspected, do not be nervous and afraid, and actively perform skin tissue biopsy, magnetic resonance examination if necessary to evaluate the degree of local recurrence. In patients with lymph node metastasis or distant metastasis, histopathology and CT should be performed to determine the diagnosis and severity of the disease [2].
Follow up every 6 months for the first 5 years after treatment and once a year thereafter, requiring lifelong follow-up. Patients with lighter skin should avoid strong sun exposure, use sunscreen that protects against UVA and UVB rays, protect clothing from the sun, and perform monthly self-skin exams.
Note: Mohs surgery is a specialized surgical technique used to remove high-risk skin cancer with a high cure rate and maximum preservation of normal tissue. In this procedure, the tumor is removed at an oblique Angle, the inclined specimen is oriented on the pattern map, sliced and frozen horizontal sections are made, and the entire peripheral and deep incisal margin of the tumor is evaluated under the microscope. The location of the residual tumor found on the histological examination is marked on the diagram to guide the subsequent stage of excision until the margin is negative.
References:
[1] PERIS K, FARGNOLI M C, GARBE C, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell carcinoma: European consensus-based interdisciplinary guidelines [J]. Eur J Cancer, 2019, 118: 10-34.
[2] Skin Tumor Research Center, Dermatologic Venereology Branch, Chinese Medical Association, Skin Tumor Group, Dermatology Branch, Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Expert Consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of basal cell carcinoma of the skin (2021) [J]. Chinese Journal of Dermatology Journal of Science, 2021, 54(9): 757-64.
(The opinions expressed here are those of the author.)


