Trends in primary drug-resistant tuberculosis in the elderly in Shandong Province, China, 2004-2019
China is one of the 22 countries in the world with a serious tuberculosis epidemic, and it is also one of the 27 countries in the world with a serious multi-drug resistant tuberculosis epidemic. Tuberculosis, especially drug-resistant tuberculosis, seriously threatens the health of Chinese people, and brings a huge burden to the elderly population. On March 24, World Tuberculosis Day, the Respiratory Branch of the Chinese Geriatric Society introduced a retrospective study on drug-resistant tuberculosis in the elderly, from the Shandong Chest Hospital and Shandong Provincial Hospital, etc., published in the journal Infectioius and Drug Resistance in 2020, DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S277203.

Research Background: With the aging of the population, the problem of drug-resistant tuberculosis in elderly patients has become increasingly prominent, which makes China's medical and health services face a heavy burden, and this problem is also a major difficulty in the global tuberculosis prevention and control. So far, there are still limited studies on age-resistant TB in China. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the epidemiological characteristics and changing trends of drug-resistant tuberculosis in the elderly.
Methods: This is a retrospective study of 12661 TB patients in Shandong Province from 2004 to 2019, of whom 4368 were elderly patients (≥60 years old). The clinical data of the above patients were collected from 36 TB prevention and control institutes in Shandong Province, including age, gender, cavity, smoking, drinking, comorbidities and drug resistance data. Sputum of patients was collected in their respective prevention and control stations, and further drug resistance detection was carried out according to the laboratory standard of Shandong Chest Hospital. Descriptive statistical analysis, Chi-square test, linear regression and other methods were used for data processing.
Results: Among 4368 cases of aged primary tuberculosis, the proportion of drug-resistant tuberculosis and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis was 17.19% and 2.29%, respectively. From 2004 to 2019, the proportion of MDR-TB increased by 160%, MDR-TB by 18.18%, Rifampicin-resistant TB by 231.82%, and the proportion of primary drug-resistant TB with cavities increased by 255%. From 2004 to 2019, the characteristics of the elderly drug-resistant TB population changed from 85.19% to 89.06% in males, the proportion of patients with cavities increased from 7.41% to 46.88%, rifampicin resistance increased from 3.70% to 21.88%, and streptomycin resistance increased from 37.04% to 62.5%. The above changes were statistically significant (P<0.05). At the same time, the proportion of females decreased from 14.81% to 10.94%, the proportion of patients without cavity decreased from 92.59% to 32.81%, and the resistance to isoniazid decreased from 66.67% to 57.81%, with statistical differences (P<0.05). The above trends are shown in Figure 1.
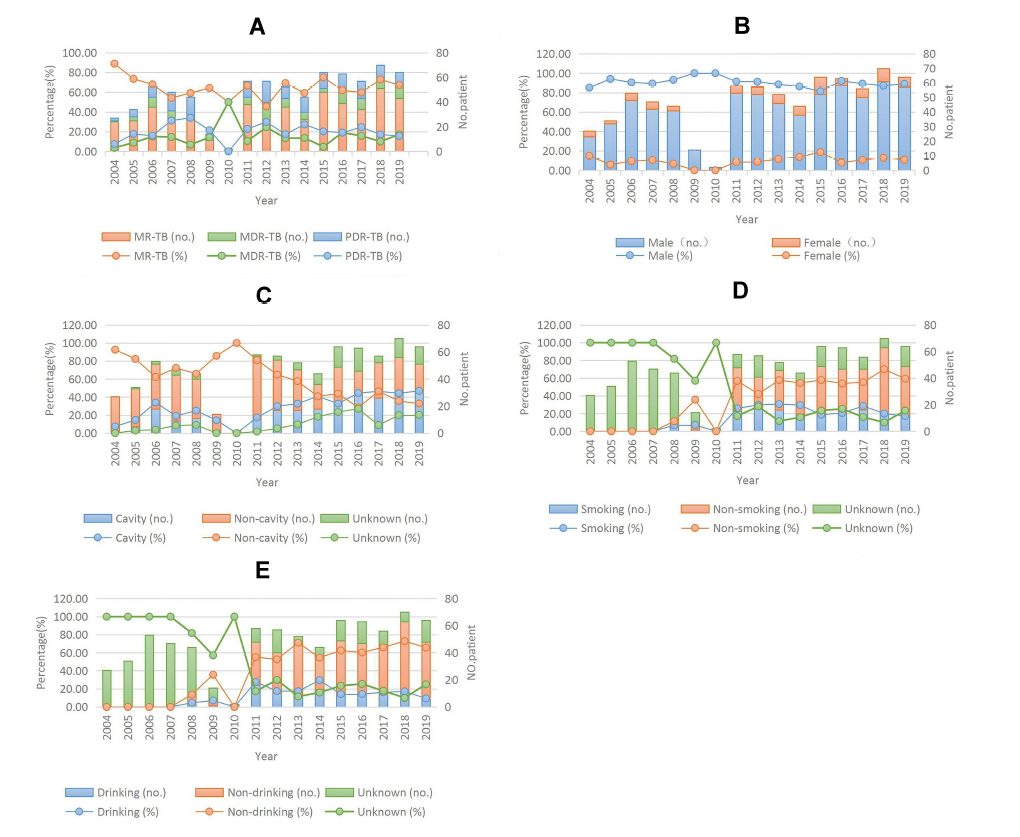
Figure 1. Trends in the number and proportion of different subgroups of primary drug-resistant tuberculosis in the elderly in Shandong, China from 2004 to 2019
A. Different types of drug resistance; B. Gender; C. Whether to incorporate voids; D. Whether or not you smoke; E. Alcohol consumption.
MR-TB, single drug resistant tuberculosis; MDR-TB, multidrug-resistant tuberculosis; PDR-TB: multidrug-resistant tuberculosis.
Conclusion: MDR-TB, MDR-TB and MDR-TB with cavity increased significantly in the aged population. Among them, the evolution trend of drug-resistant tuberculosis showed an increase in males, easy to combine cavity, and the risk of rifampicin resistance and streptomycin resistance increased. In order to better control drug-resistant TB in the elderly population in the future, we should pay more attention to the population with male, smoking history, drinking history, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and diabetes, and take more targeted treatment measures for these subgroups.

