[Micro Science Popularization] Exploring Filamentous Warts
1.· Understanding filamentous warts: Appearance, characteristics, is it contagious? please
Have you ever noticed that you have "little bumps" on your face or neck or under your arms? Many people may even date back to more than ten years, and self-report that there are gradually increasing and increasing sarcomatous protrusions, and even infect people who live with them. In fact, this is a medical wart called a filiform wart, which belongs to a special type of common wart called "瘊" and "wart". It is found in loose areas such as the neck, forehead, around the eyelids, and under the arms. Filamentous warts are mainly manifested as skin color, light brown, light gray wart-like protrusions, rough surface, hard texture. Some small partners may wonder whether filamentous warts can be contagious? The answer is yes. Filamentous warts are mainly transmitted by direct or indirect contact, when people come into contact with patients or items with HPV, just when the skin mucosa has a small damage or reduced immunity, HPV may invade the skin to form warts, in addition to sharing towels, close clothing and other indirect contact infection is also easy to infect.
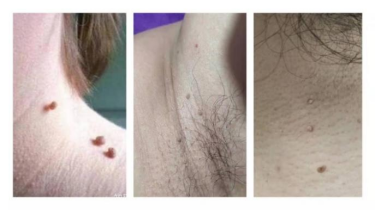
Quotations from https://m.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_16002326
2.· Why do you get filamentous warts: Is HPV virus infection?
Filamentous warts are benign growths caused by human papillomavirus HPV (types 1, 2, 4, 7, and 26-29) infecting the mucous membranes of the skin.
· Is it related to HPV vaccination? !
At present, there are more than 200 HPV viruses isolated from the human body, which are usually divided into low-risk and high-risk types. [2][3] Low-risk HPV includes HPV6, 11, 40, 42, 43, 44, etc., which can cause condyloma acuminatum and common warts. High-risk HPV types include HPV16, 18, 31, 33, 35, etc., which can lead to low cervical cell abnormalities, high cervical cell abnormalities (precancerous lesions) and cancers (such as cervical cancer, rectal cancer, oral cancer, tonsil cancer, vulvar cancer, anal cancer, prostate cancer, bladder cancer, etc.). HPV vaccine generally can only prevent part of the human papillomavirus, including bivalent vaccine (prevention of HPV16, 18), quadrivalent vaccine (prevention of HPV6, 11, 16, 18, and caused by genital warts, precancerous lesions, cervical cancer and other lesions), Nine-valent vaccine (to prevent HPV6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, 58 types, can effectively prevent 80%~90% of the corresponding type of virus caused by cervical cancer, condyloma acuminatum, vaginal cancer, vulvar cancer, anal cancer and other related diseases). [4] Therefore, the vaccine can not prevent all human papillomavirus, some patients after the injection of HPV vaccine warts are normal, but the possibility of infection will be reduced.
3.· Viral warts family: filamentous warts, flat warts, common warts, condyloma acuminatum, skin tags...... How to tell the difference? please
Modern people's fast pace of life, high pressure, stay up late frequently lead to low resistance, a little attention to hygiene or small wounds on the body, flat warts, ordinary warts will come to the door. Speaking of this, the small partners are curious that these are warts, a little unclear, then how should we identify?
① Flat warts occur on the face, the back of the hand and the forearm of children and adolescents, usually manifested as light brown flat elevated papules, with smooth surface, hard quality, a large number and dense, and the skin lesions are bead-like arrangement after scratching (autoinoculation reaction or Koebner phenomenon).
Common warts can occur on all parts of the body, but are more common in the hand, usually manifested as one or more solid convex dome-shaped soybean size of taupe or skin papules, touch the surface has a rough feeling.
③ Condyloma acuminatum is usually caused by sexual contact and is manifested as soft papules or plaques on the external genitals, perianal, perineum or groin
④ Skin warts, also known as soft verruca, are pedicled skin papules, mainly occurring in the middle and old age, one of the types is also filamentous, similar to filamentous warts, but the surface is smooth and not rough, not warty, the size of rice grains, under the microscope only shows the process of the epidermis and the thickening of the spine layer, which can be distinguished from filamentous warts.
Molluscum contagiosum skin lesions can occur in any part, children are most likely to be on the back of the hands, limbs, trunk and face, adults through sexual contact can be seen in the genitals and buttocks. It usually appears as a waxy glossy papule or nodule with a concave tip that extrudes a cheesy molluscum body.
4. What inspection should I do if I suspect that I have filiform warts? please
Typical filamentous warts can be diagnosed by the clinician's visit, and the warts can be further enlarged by the dermoscope, which shows a rough surface of gray filamentous warts, with white pus at the tail of the filamentous warts, and may be accompanied by bleeding points or blood vessel dilation. For atypical lesions (suspected precancer or cancer) and cases with uncertain diagnosis, pathological examination is rarely recommended. Pathological examination is the gold standard for the diagnosis of filamentous warts, which takes tissue from the affected part of the patient and is observed under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis. [1]
5. If confirmed filamentous wart, how to treat better? Can you just grab it with your hands? Will the ointment help? please
It has been reported that some filamentous warts can be resolved by themselves without treatment, but it is almost difficult to observe cases of spontaneous regression in clinical practice, and most people's disease course can even last for decades. If filamentous warts appear uncomfortable symptoms or patients feel that the impact of beauty should be promptly to the hospital for treatment. Here are some common treatments. [5]
(1) Topical drugs: Those with large skin lesions or who are not suitable for physical therapy can be treated with topical drugs, and the commonly used concentration is 17% salicylic acid, which is recommended to be used daily for 7-12 weeks. Drugs such as retinoic acid ointment and imiquimod cream can also be used to treat the disease. However, due to the poor efficacy of topical drugs and easy recurrence, physical therapy is recommended in clinical practice, such as freezing, laser and electric burning.
(2) cryotherapy: The warts with small lesions and a small number of warts can be cryotherapy, generally treated once every 1-2 weeks, and most warts can be subsided after 2-3 treatments. The elimination rate of combined cryotherapy and salicylic acid therapy was higher than that of monotherapy. The advantages are simple operation, non-invasive and quick recovery. However, side effects may include pain, blisters, hyperpigmentation or loss of color.
(3) CO2 laser: cautery gasification after local anesthesia, time 0.5 ~ 2 minutes. Compared to cryotherapy, laser treatment can more precisely locate the lesion area and reduce the impact on the surrounding normal skin. But it may cause redness and mild pain.
(4) Electric burning: the use of safe and moderate current to remove the diseased tissue, and then spark discharge cautery to remove the remaining warts, so that it necrosis, fall off. But it can cause pain, scarring, burns, infections, etc.
(5) Injection: The injection of interferon in the warts, such as Siruojin and Yunde, can directly act on the virus and improve the therapeutic effect.
(6) Other: if the wart is large and difficult to deal with or the effect of physical therapy is not good, you can take surgery to remove the wart, the effect is more significant. However, there may be a risk of wound infection, bleeding and other complications after surgery.
Some small partners may use their hands to pull down filamentous warts, which will not only cause skin damage and secondary infection, but also lead to their own planting, the longer the HPV virus spreads to other parts, aggravating the condition. So don't use your hands to pull!
In particular, according to published guidelines, most patients whose warts disappear on their own or after treatment such as freezing with topical agents are prone to frequent recurrence. Treatment may reduce the infectivity of HPV, but it does not necessarily eradicate HPV. For subclinical infections, it is recommended to more actively implement cryotherapy, local imiquimod application, if necessary, can consider laser electric burning, and interferon injection, photodynamic therapy (extended to 1 cm around the wart) and other methods to reduce the recurrence rate.
6.· Can Filiform warts be prevented? please
HPV is widespread in nature, so how do we prevent it? HPV can enter the human body through the skin damage to induce filamentous warts, so the prevention of filamentous warts needs to do the following: ① Do a good job of protection during activity, avoid trauma, can prevent infection. ② Avoid close contact with people suffering from filamentous warts, and do not share daily necessities with them, such as towels, sheets, etc. In addition, to maintain good living habits, avoid staying up late, appropriate aerobic exercise, such as cycling, jumping rope, jogging, etc., help to improve immunity.
References:
[1]Zhu P, Qi R Q, Yang Y, et al. Clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous warts (2022)[J]. Journal of Evidence‐Based Medicine, 2022, 15(3): 284-301.
[2]Goldstein B G, Goldstein A O, Morris-Jones R, et al. Cutaneous Warts (common, plantar, and flat warts)[J]. UpToDate. [updated 7 Mar 2018; cited 29 Jan 2019], 2018.
[3]Palefsky J M, Hirsch M S, Bloom A. Human papillomavirus infections: Epidemiology and disease associations[J]. Waltham: UpToDate, 2018.
[4]Roden, R., Stern, P. Opportunities and challenges for human papillomavirus vaccination in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 18, 240-254 (2018)
[5]Kore VB, Anjankar A. A Comprehensive Review of Treatment Approaches for Cutaneous and Genital Warts. Cureus. 2023 Oct 25; 15(10):e47685. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47685. PMID: 38022045; PMCID: PMC10673707.

