[Micro Science Popularization] Intelligent Innovation of Nutrition Management for the Elderly Helps Intelligent Medical Care and Improve the Quality of Life for the Elderly!
Introduction: Meeting the challenges of aging
China is rapidly aging, and the increase in the number of elderly people makes effectively managing their nutritional status a major public health challenge. Older people often face more complex nutritional needs due to changes in physiological functions, the prevalence of chronic diseases and mental health problems. However, the traditional nutrition management model is difficult to meet these special needs due to incomplete information collection, insufficient personalized services, and imperfect monitoring and feedback mechanism.
As an emerging health management tool, the smart medical and nursing combined platform uses big data, cloud computing and artificial intelligence technology to provide personalized and comprehensive nutrition management services for elderly patients. This article will explore how this platform can be effectively applied to the nutrition management of elderly patients to improve their quality of life and health.
Second, background analysis: the particularity of the nutritional needs of the elderly
With the growth of age, the digestion and absorption function and metabolic rate of elderly friends will be reduced, and the demand for nutrition will also change. They may need more protein, but their ability to absorb trace elements such as calcium and vitamin D may be reduced. In addition, chronic diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease, as well as mental health issues such as loneliness and depression, can affect their diet and nutrient intake.
Third, smart medical and nursing combined platform: the new assistant of nutrition management
The development of the smart medical and nursing combined platform provides a new solution for the elderly nutrition management. Based on modern technology, it connects medical and nutrition data, provides intelligent analysis and evaluation, personalized nutrition services, and remote monitoring and feedback.
Application framework: Three-step strategy
1. Data collection and integration
Through questionnaire survey and interview, elderly patients' living habits, eating habits and other information were collected, and the data was shared with medical institutions to realize the interconnection of medical and nutrition data. These data, including but not limited to elderly patients' weight, dietary intake, albumin levels, nutritional screening assessment scales, etc., provide the basis for intelligent analysis.
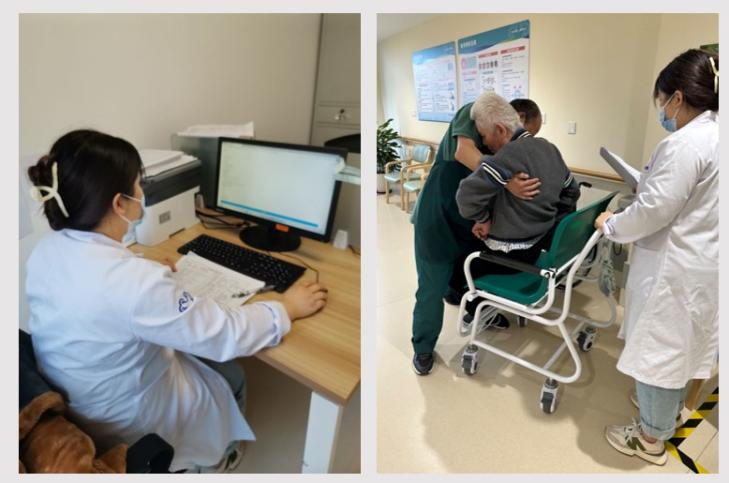
Figure 1 Data collection and file entry
2. Intelligent analysis and evaluation
The algorithm was used to analyze nutritional data, assess the nutritional status of elderly patients, and identify potential nutritional risks and problems. Based on the analysis results, personalized nutrition recommendations and diet recommendations are generated. Combined with nutritionist manual audit can not only help elderly patients understand their own nutritional needs, but also provide scientific basis for medical institutions to optimize nutrition intervention programs.

Figure 2 Nutrition management services supported by the platform APP
3. Personalized nutrition service
Based on the evaluation results, the smart health care platform can provide customized nutrition programs and ensure the effective implementation of nutrition programs through real-time feedback with bed doctors.
FIG. 3 The nutritionist uses mobile terminal for quick rounds/remote access
Fourth, challenges and countermeasures
The application of smart medical and nursing combined platform in elderly nutrition management faces challenges such as data privacy protection, technology popularization and acceptance, and shortage of medical resources and talents.
Data privacy and security: Strengthen data protection to ensure the security of user information.
Technology popularization and acceptance: Through publicity and training, improve the awareness and use of the platform by elderly friends and their families.
Shortage of medical resources and talents: Train professionals, optimize resource allocation, and benefit more elderly friends.
V. Conclusion and prospect
The application of the intelligent medical and nursing combined platform in the nutrition management of the elderly has shown great potential and value. It can not only provide scientific and comprehensive nutrition management, but also significantly improve the quality of life and health of elderly friends.
Looking to the future, the smart medical and nursing combined platform needs more cross-field cooperation and technological innovation to meet the diverse needs of elderly friends. With the advancement of technology and the promotion of applications, this platform is expected to play a greater role in elderly nutrition management and provide effective solutions for dealing with an aging society.
The smart medical and nursing combined platform is a new nutrition and health partner for elderly friends. Let's look forward to the positive changes it will bring.
References:
[1] Guo Jing, Zhang Lingzhi. Construction and management of home health care service system combined with medical care [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2018,53 (7) : 773-777. (in Chinese)
[2] Liu Hao, Zou Ling. Discussion on a new model of intelligent medical care based on Internet + [J]. China Hospital Management, 2018,38 (5) :56-57. (in Chinese)
[3] Wan Junli, Bian Wei. Application of artificial intelligence in the field of accurate nutrition management of chronic disease patients [J]. Military Nursing, 2023,40 (10) : 92-95. (in Chinese)
[4] Pang Shu, Sun Haonong. Research progress of artificial intelligence in the field of geriatric nutrition [J]. Practical Gerontology, 2024,38 (2)
: 109-113.
[5] Zhang L, Huang X, et al. Screening effect of anthropometric indicators on risk assessment of malnutrition in elderly hospitalized patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 2018, 44 (4) : 984-987.



