[Micro Popular Science] Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is a skin tumor that occurs in the basal layer cells of the epidermis or hair follicle, and is the most common skin malignancy, with a relatively high incidence in the elderly. But fortunately it is less malignant, usually slow growth, although with local destruction, but rarely physical metastasis.
Why does the skin become malignant and basal cell carcinoma occurs?
Basal cell carcinoma originates from keratinocytes in the basal layer of the skin epidermis. It grows slowly and rarely metastasizes, but is locally aggressive and can cause damage to surrounding tissue. The most common cause is UV exposure, which is the most important risk factor. In the elderly, accumulated UV damage from long-term exposure to the sun increases the risk of disease. For example, farmers, fishermen and other people engaged in outdoor work for a long time, the skin is exposed to ultraviolet radiation for a long time, and the incidence of basal cell carcinoma is higher. Light skin, multiple sunburns, a family history of skin cancer, ionizing radiation, and exposure to chemical carcinogens (especially arsenic) are also common causes.
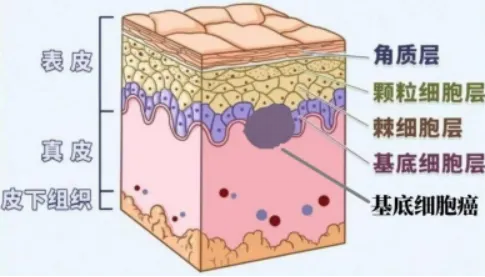
What does basal cell carcinoma look like?
Basal cell carcinoma occurs in the head and face, especially in the nose, eyelids, cheeks and other exposure areas. This is because these areas are more susceptible to direct exposure to ultraviolet light. It can also occur in other parts of the body, such as the neck, the back of the hands, etc.
Basal cell carcinoma comes in many forms. The most common is the nodular ulcer type, the skin lesions are initially gray or waxy small nodules, hard in texture, slowly increasing, the central ulcer can appear, the edge of the ulcer is pearl-like uplift, known as erosion ulcer. This type of ulcer is usually not painful, but gradually erodes the surrounding tissue. The second is the pigmented type, which contains more pigment in the basal cell carcinomatosis and appears as brown or black nodules or plaques, which is easily misdiagnosed as melanoma. The superficial type is one or more erythematous squamous patches with clear boundaries, slight infiltration, small superficial erosion or scab visible on the surface, slow growth, and slow expansion to the periphery.
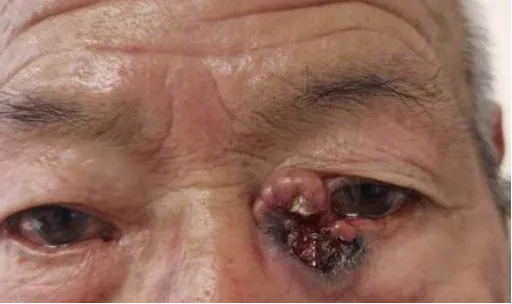
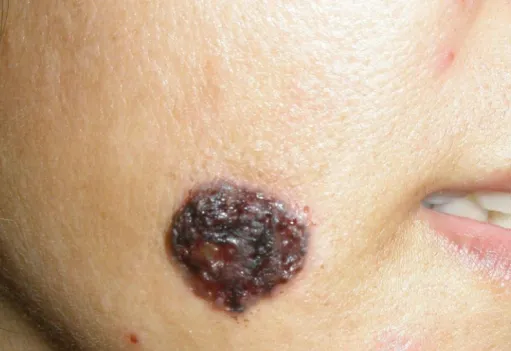
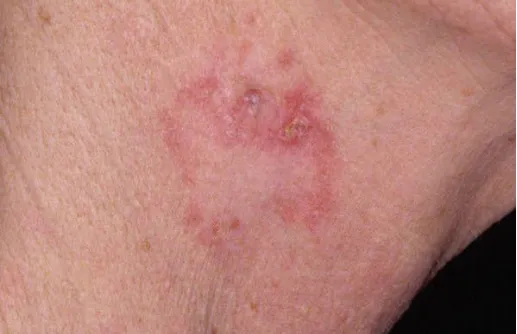
How is basal cell carcinoma diagnosed?
Pathological examination is the gold standard for diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma. The typical histopathological manifestation of basal cell carcinoma is a tumor cell mass composed of basal-like cells with surrounding cells arranged in a palisade pattern.
How to treat basal cell carcinoma?
Surgical resection is the main treatment for basal cell carcinoma. For smaller, localized tumors, they can usually be completely removed with surgery. During surgery, the doctor will extend the resection area at the edge of the tumor to ensure complete removal of tumor cells, and perform skin grafting or flap repair in the tissue defect area.
For some elderly patients who cannot tolerate surgery, such as those with serious heart and lung disease, radiation therapy is an effective alternative. It can damage the DNA of tumor cells, preventing them from growing and dividing. However, radiation therapy may cause some skin reactions, such as erythema, pigmentation, and atrophy of the skin, and its long-term effects may lead to local tissue fibrosis. Early superficial basal cell carcinoma may also be treated with photodynamic therapy.
Frozen, topical drugs such as imiquimod cream are commonly used as adjuvant therapy.
Can basal cell carcinoma be cured?
The prognosis of basal cell carcinoma is generally good, especially if detected and treated early. Most patients are completely cured with proper treatment. However, if the tumor has invaded deep tissues, such as bones, nerves, etc., or is not treated in time, it may lead to serious damage to local tissues, causing dysfunction, such as basal cell carcinoma of the eyelid, which may affect vision.
How to prevent basal cell carcinoma?
Sun protection is the key to preventing basal cell carcinoma. The elderly should try to avoid going out during the time when the ultraviolet rays are strongest (10 am to 4 PM). If you have to go outside, you should use a sunshade, a wide-brimmed hat, sunglasses and other protective equipment, and wear sunscreen with a sun protection index (SPF) of at least 30, and take care to reapply regularly.
In addition, perform regular skin self-examinations, especially for areas that are easily exposed to the sun, and seek medical attention as soon as abnormal skin nodules or patches are found.
Basal cell carcinoma can be prevented and treated, although it is a skin malignant tumor, but its degree of malignancy is low, not easy to metastasization, so the elderly do not need to talk about cancer color change, as long as early detection, early treatment, most of the basal cell carcinoma can be completely cured. Therefore, it is necessary to objectively and correctly understand the disease, avoid negative mentality, choose regular medical institutions, cooperate with the examination, and actively treat.
Li Weiran, Young member of the Dermatology Branch of Chinese Geriatric Society, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University
(The opinions expressed are solely those of the author. Some pictures in this article are from the Internet, if there is infringement, contact delete)

