"Love and Hatred" of Cervical Cancer and HPV
The love-hate relationship between Cervical cancer and HPV
Cervical cancer is the fourth largest malignant tumor affecting women's health in the world and the second largest female malignant tumor in China. According to statistics, in 2018, there were nearly 110,000 new cases of cervical cancer in China, and nearly 50,000 deaths, among which the peak age of new cases was 20-24 years old, showing a younger trend. Without effective action, cervical cancer deaths will increase by 50% by 2030. Human papillomavirus-related diseases such as cervical cancer have become a serious threat to human health.
Why do you say to eliminate cervical cancer? Because cervical cancer is one of the only cancers with a clear cause, we just need to remember that persistent infection with high-risk human papillomavirus HPV is the main cause of cervical cancer and its precancerous lesions.

Let's get to know human papillomavirus, English HPV, it is a double-stranded DNA virus, with a high degree of mucosal epithelial characteristics, there are about 200 types of subtypes identified from the human body, according to the main infection site is divided into skin type and mucosal type, but we usually refer to its carcinogenic potential, divided into low-risk and high-risk types. Low-risk types are mainly 6 and 11, mainly causing genital warts and benign lesions, high-risk types are mainly causing cervical cancer, anal cancer, genital cancer, etc., the common is 16 and 18, and more than 90% of cervical cancer are closely related.
How is HPV transmitted? Sex is the main route to HPV infection, but not the only one. HPV infection can also be contracted through direct contact. For example, in daily life, hands come into contact with things with HPV, when going to the toilet, bathing will inadvertently bring the virus into the genital organs, or the genital organs directly contact with bath towels, bathtubs, toilets and other items with HPV can be transmitted HPV, so the chance of infection with HPV is very large.

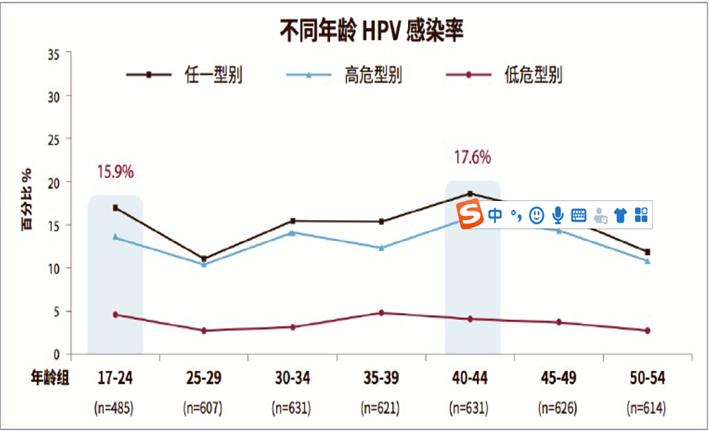
Data show that about 80% of women have HPV infection at some point in their lives, but most HPV infections are one-time, because the body will automatically clear the virus, so the most common outcome of HPV infection is about 70% of HPV infection will be resolved within 1 year, 90% will be resolved within 2 years. Only persistent high-risk HPV infection is likely to lead to cervical precancerous lesions, or even progressive cervical cancer. This process is very long, usually 10-15 years.
Don't panic! As long as attention is paid to HPV infection, no big deal :WHO The recommended comprehensive prevention and control strategy for cervical cancer includes tertiary prevention, primary prevention is mainly health education and vaccination health education is mainly to popularize HPV-related knowledge, improve the awareness of safe sex, eliminate the fear and shame of HPV infection and related diseases, and improve the knowledge and skills of medical staff on the prevention and control of HPV infection and related diseases. Secondary prevention is what we call "three early" in the early clinical stage of the disease, through the adoption of early detection, early diagnosis, early treatment of the three early preventive measures to control the development and deterioration of the disease. Tertiary prevention is to carry out appropriate surgery, chemoradiation and palliative therapy according to clinical stages.
Let's take a look at the primary prevention of HPV vaccine, the significance of vaccination is to prevent HPV infection caused by the disease, reduce the burden of cervical cancer.

Currently, there are three types of HPV vaccines on the global market: bivalent, four-valent and nine-valent, and the "price"; represents the type of virus that can be prevented by the vaccine. A bivalent vaccine that protects against infection by HPV16 and HPV18 viruses. The quadrivalent vaccine protects against HPV types 6, 11, 16, and 18. Bivalent is for women between the ages of 9 and 45, and quadvalent is for women between the ages of 20 and 45. The nine-valent vaccine is against the nine subtypes of HPV6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, 58. It is usually given in 3 injections for a total of 6 months to be effective. The bivalent vaccine was administered at 0, 1 and 6 months. The quadrivalent and nine-valent vaccines are administered at 0, 2, and 6 months. At present, the bivalent and quadrivalent vaccines on the domestic market can prevent and control 70% of cervical cancer risk, while the nine-valent vaccine can prevent 90% of cervical cancer. The public can choose to receive different HPV vaccines according to their age and economic status.
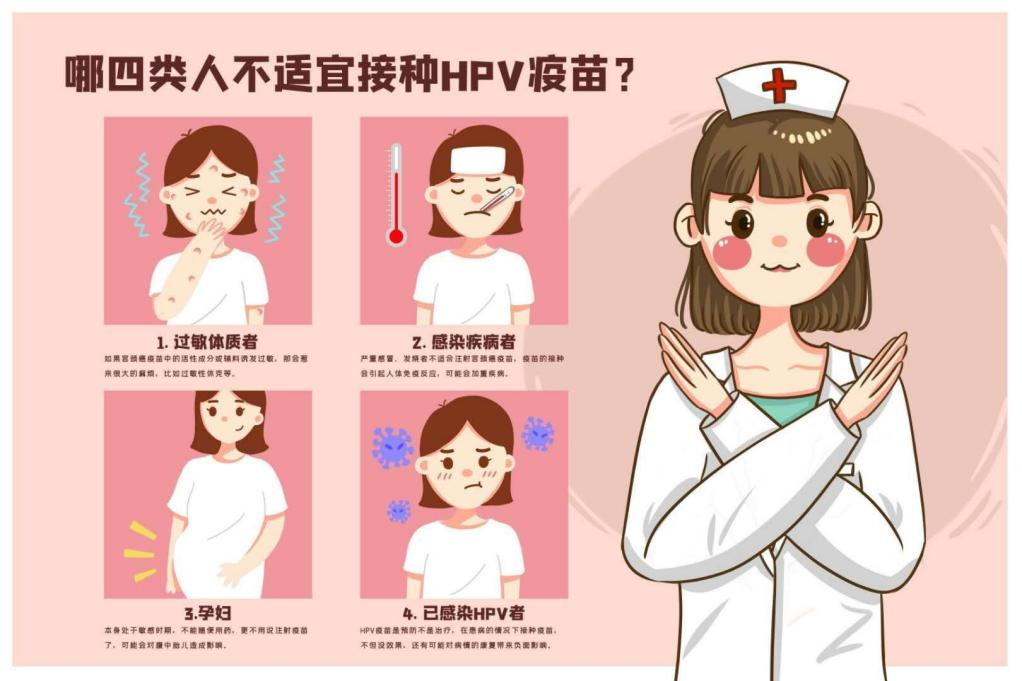
Who can not vaccinate, one is allergic, and then infected with disease patients, that is, pregnant women, and then has been infected with HPV, the vaccine has no effect.
Can you not get cervical cancer after getting HPV vaccine? Should cervical cancer screening be done after vaccination? Whether the vaccine is 2-valent, 4-valent or 9-valent, regular screening is still required after vaccination. Existing vaccines, including the 9-valent vaccine, do not protect against all high-risk HPV types. Moreover, there may be a small number of high-risk HPV types that are not currently identified, and of course there is no targeted vaccine.
On July 6, 2021, WHO issued the latest guidelines for screening and treatment of cervical precancerous lesions to optimize diagnostic tools and screening options, promote cervical cancer prevention and save more lives, and the new guidelines recommend HPV-DNA testing as the preferred screening method for cervical cancer screening. The average woman has regular cervical cancer screening starting at the age of 30, the preferred HPV-DNA test, and regular screening every 5-10 years. If HPV-DNA testing has not yet been implemented and is still using VIA (acetic acid staining) or TCT (liquid-based cytology) as the primary screening method, regular screening is required every 3 years.

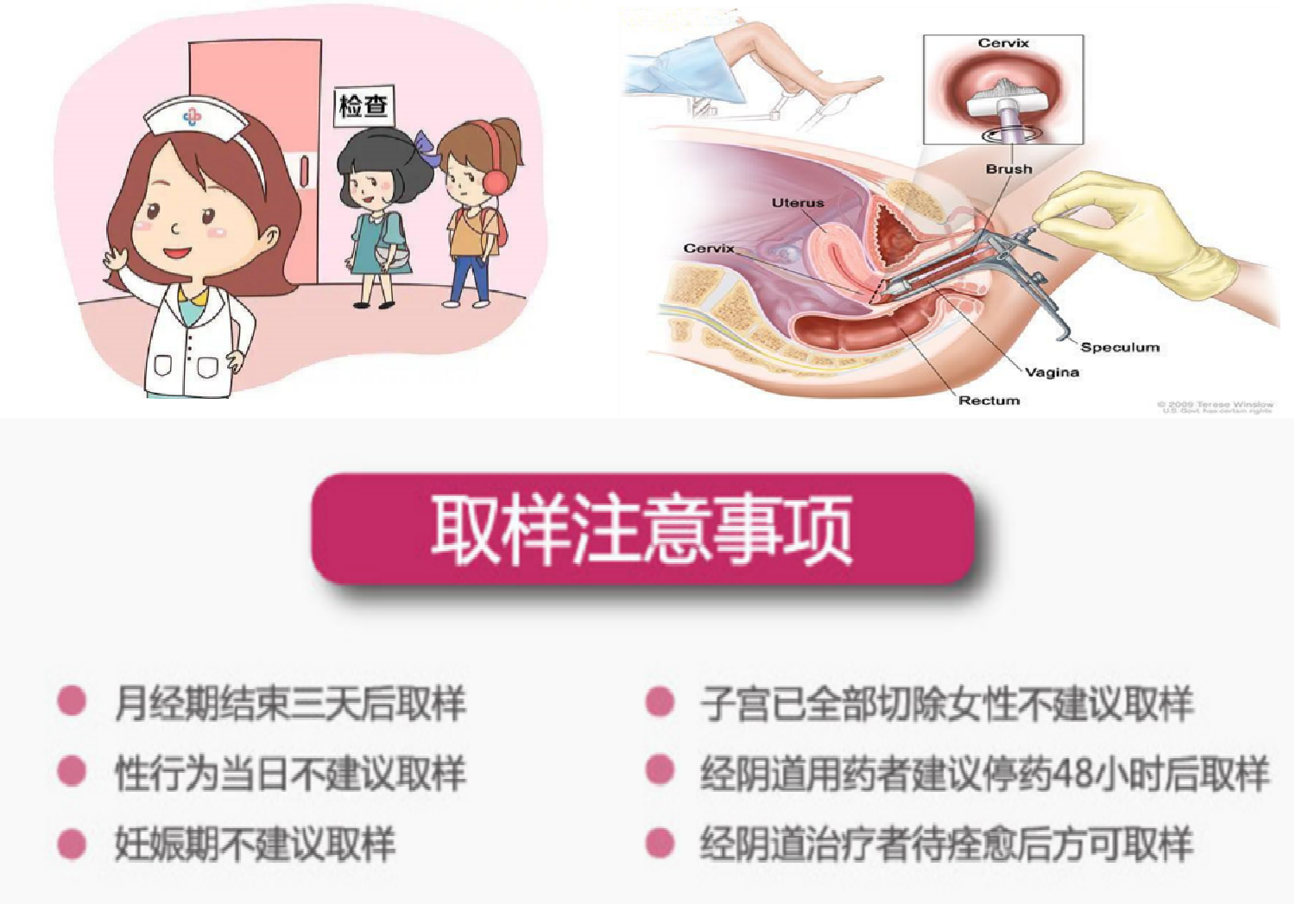
How is screening done? Everyone more or less have some fear of gynecological examination oh, in fact, this worry is completely unnecessary, our gynecologists are very experienced, and the action is very gentle, is to use a professional speculum to open the vagina, brush off cervical cells for examination.
Healthy and happy life!
Contributor: Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University Zhang Hong
Reviewer: Wang Yan, Vice President of Health Management Branch of Chinese Geriatrics Society and director of Health Examination Center of Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University

